bitmap与标签存储
最近在标签存储中,需要根据标签值查询用户id,所以想到在源数据表基础上建立索引。因为标签数据量大,且标签基数相对较少,查询条件往往涉及多标签组合过滤,所以选用了bitmap作为索引。
bitmap简介
bitmap就是以比特位来存储状态。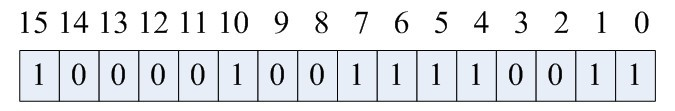
bitmap索引
例如用户数据表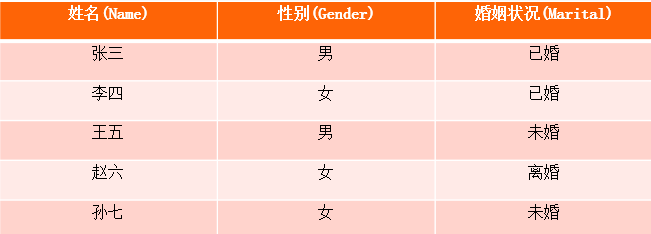
现在要在用户性别和婚姻状态建立bitmap索引。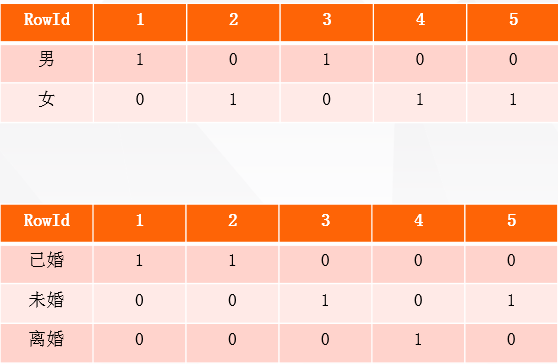
通过索引值为1,我们可以看出性别男的用户rowid为1和3,然后在查询源用户表,就可以查出性别男的是张三,王五。婚姻状况同理。
下面我们如果要查询:
select * from table where Gender=’男’ and Marital=’未婚’
首先我们找到男索引列和未婚索引列,然后对其取并集。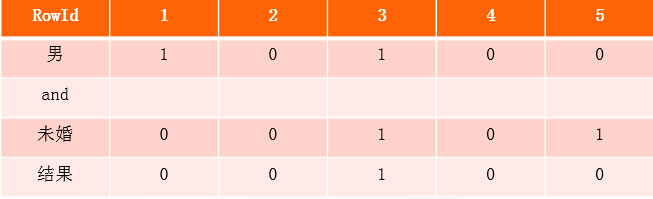
因为是bit存储,索引取并集就相当简单,只需要进行位运算&即可。所以整个bitmap索引多条件过滤效率很高。
bitmap的适用范围
因为bitmap的特性,所以bitmap索引适用于:
- 查询为主,更新较少的数据
- 基数较少,重复度较多的列
- and/or可以直接通过位运算快速得到结果。
RoaringBitmap
未压缩的bitmap占有空间大,所以提出了各种的压缩算法。如图: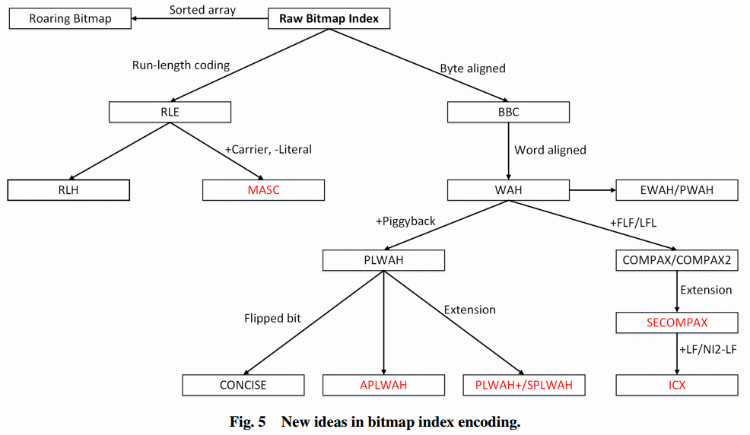
从图中可知,RoaringBitmap是基于Sorted array进行压缩。而其他压缩算法都是基于aligned或者run-length-encoded,核心思想都是把数据规整,然后采用run-length编码。
Most alternatives to Roaring are part of a larger family of compressed bitmaps that are run-length-encoded bitmaps. They identify long runs of 1s or 0s and they represent them with a marker word. If you have a local mix of 1s and 0, you use an uncompressed word.
There are many formats in this family:
- Oracle’s BBC is an obsolete format at this point: though it may provide good compression, it is likely much slower than more recent alternatives due to excessive branching.
- WAH is a patented variation on BBC that provides better performance.
- Concise is a variation on the patented WAH. It some specific instances, it can compress much better than WAH (up to 2x better), but it is generally slower.
- EWAH is both free of patent, and it is faster than all the above. On the downside, it does not compress quite as well. It is faster because it allows some form of “skipping” over uncompressed words. So though none of these formats are great at random access, EWAH is better than the alternatives.
There is a big problem with these formats however that can hurt you badly in some cases: there is no random access. If you want to check whether a given value is present in the set, you have to start from the beginning and “uncompress” the whole thing. This means that if you want to intersect a big set with a large set, you still have to uncompress the whole big set in the worst case…
从中可知,BBC、WAH、Concise、EWAH都是基于run-length-encoded算法,它们很难处理随机读,而且如果想要对两个bitmap取交集,必须解压整个大集合。
基于这些问题,RoaringBitmap提出了另一种压缩方法。

图中展示了RoaringBitmap的结构,每个RoaringBitmap中都包含一个RoaringArray,名字叫highLowContainer。
highLowContainer存储了RoaringBitmap中的全部数据。
RoaringArray highLowContainer;
具体的讲解可以参照RoaringBitmap数据结构及原理这篇文章。
RoaringBitmap在设计中结合了Array与Bitmap存储,当数据稀疏时,Array存储会更节省空间(试想[3,10000,200000]这三个数如果用bitmap存储会消耗空间远大于直接存储这三个的数组),当数据稠密时,bitmap存储节省空间。而且还提供了RunContainer利用run-length-encoded算法进行压缩(只有在调用runOptimize()方法才会发生转换,会分别和ArrayContainer、BitmapContainer比较空间占用大小,然后选择是否转换)。
标签
基于用户的行为,对用户的特征进行抽象,使用标签来反映用户的动作与特征。在用户画像中,常常需要根据用户标签去对用户做特定的运营或者活动。
在存储上,考虑到用户标签的不同,如果将所以标签类别作为一张宽表(类似星型模型),将会是个很稀疏的表,且随时面临着标签的增长,所以在存储上选择了Hbase。
而通过某些标签筛选出特定用户是个很常见的需求。而Hbase查询如果不是通过rowkey查询的化,都是scan全表,效率很低。而标签相对于用户数量而言基数较少,且常有根据多个标签组合查询(and或者or),所以想到了将标签使用bitmap索引存储。
所以在标签数据组织上,有个正排的标签表,用户id作为rowkey,主要方便查询用户的标签值。一个标签对应的bitmap索引表,用于通过标签组合过滤查询用户。
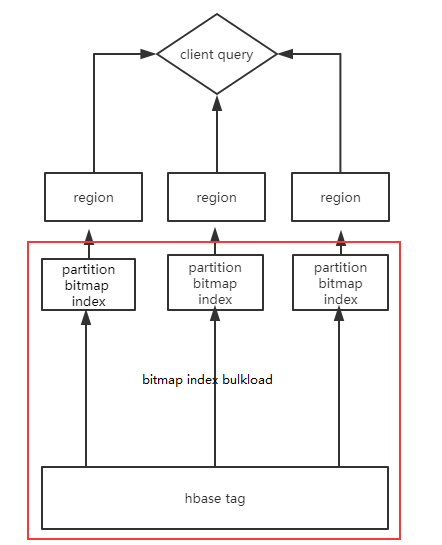
将tag表中的用户-标签数据,首先通过hash(uid)做分区,在对同一tag的数据做bitmap index(红色方框)。不同的partition数据分布于hbase的region中。在查询的时候通过协处理器并行查询各个region,最后将数据返回给client。其中进行partition主要是为了:有些标签所覆盖的用户很广,甚至上千万或者上亿,整个bitmap占用的空间会很大,对index构建和查询带来效率问题;划分region后,通过hbase的协处理器可以并发的查询,每个region返回的bitmap也更小,效率更高。
总结
bitmap提供了不一样的数据存储,以及高效的运算,成为了某些场景下的利刃。比如在标签存储中,可以很好的使用bitmap对标签组合查询用户。但bitmap并非银弹,如果是基数较高或者更新频繁的系统中,似乎并不是很好的方案。但bitmap给予我们提供了一种不同的视角,散列却又聚集。