airflow使用指南
airflow 是一个编排、调度和监控workflow的平台,由Airbnb开源。airflow 将workflow编排为tasks组成的DAGs,调度器在一组workers上按照指定的依赖关系执行tasks。同时,airflow 提供了丰富的命令行工具和简单易用的用户界面以便用户查看和操作,并且airflow提供了监控和报警系统。
airflow 核心概念
- DAGs:即有向无环图(Directed Acyclic Graph),将所有需要运行的tasks按照依赖关系组织起来,描述的是所有tasks执行的顺序。
- Operators:可以简单理解为一个class,描述了DAG中一个具体的task具体要做的事。其中,airflow内置了很多operators,如BashOperator 执行一个bash 命令,PythonOperator 调用任意的Python 函数,EmailOperator 用于发送邮件,HTTPOperator 用于发送HTTP请求, SqlOperator 用于执行SQL命令…同时,用户可以自定义Operator,这给用户提供了极大的便利性。
- Tasks:Task 是 Operator的一个实例,也就是DAGs中的一个node。
- Task Instance:task的一次运行。task instance 有自己的状态,包括”running”, “success”, “failed”, “skipped”, “up for retry”等。
- Task Relationships:DAGs中的不同Tasks之间可以有依赖关系,如 TaskA >> TaskB,表明TaskB依赖于TaskA。
通过将DAGs和Operators结合起来,用户就可以创建各种复杂的 workflow了。
operators
下面讲解下常见的operator,以及如何使用,注意点。
BashOperator
1 | run_this = BashOperator( |
很简单的一个operator,执行bash命令。其中bash命令返回状态码0时,表示此task成功;否则,失败。
PythonOperator
1 | run_this = PythonOperator( |
顾名思义,就是执行python函数。参数通过op_kwargs传递。如果想要任务失败,需要raise ValueError。
BranchPythonOperator
1 | options = ['branch_a', 'branch_b', 'branch_c', 'branch_d'] |
分支操作,通过python_callable返回值选定下一个依赖执行的task,即python_callable返回值等于下一个依赖task的task_id,而其他未被选中的task,则会被skipped。如果在task后面还有依赖join,此时需要将join的trigger_rule设置为‘one_success’ ,如下图所示:
SubDagOperator
当dag中某部分tasks结构完整,功能统一,能够独立提供某项流程时。就像软件开发中模块划分一样,我们也希望将这部分task依赖抽离出来,独立成为单一的DAG,且能够很好的嵌入其他DAG,完成整个流程。这便出现了subDag。
1 | section_1 = SubDagOperator( |
其中subdag是个函数,返回Dag实例。假如subDag为Dag A,那么A的dag_id必须为parentDag的dag_id+ ‘.’ + subdag_id。即
1 | dag_subdag = DAG( |
添加subDag后的Dag如: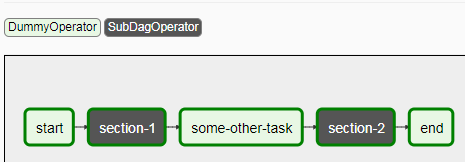
select-1作为是Dag的一个task,内部则是一个subDag,也有完整的task任务关系。
TriggerDagRunOperator
1 | trigger = TriggerDagRunOperator( |
此operator执行了python_callable对应的方法后,会触发trigger_dag_id对应的dag执行,并通过conditionally_trigger函数中的参数(xxx_obj)将参数传递给trigger_dag,trigger_dag通过kwargs获取到xxx参数。此operator在不影响原来的任务依赖下,能够触发额外的操作,具体使用可根据场景进行选择。
scheduler
除了配置task的operator,还需要对整个dag配置调度和触发的限制条件。
DAG RUN
- schedule_interval:调度控制。None代表不会被schedule,只能外部触发;@once只会被schedule触发一次。其他即可通过cron表达式设置。
- Backfill and Catchup:如果DAG设置有start_date(python datetime),且schedule_interval定义了调度周期,那么有个问题,是否需要从start_date按照schedule_interval调度执行到最新时间,或者配置的end_date。这个通过catchup参数配置,catchup=False表示不调度执行历史,只会在DAG创建时执行最近一次的schedule_interval。默认catchup=True
task dependency
trigger_rule:
- all_success: (default) 所有的父任务都成功
- all_failed: 所有的父任务都失败
- all_done: 所有父任务都已经执行完
- one_failed: 只要有一个父任务失败,就执行,不需要等所有的父任务失败
- one_success: 只要有一个父任务成功,就执行,不需要等所有的父任务成功
- dummy: dependencies are just for show, trigger at will
xcoms
xcoms让task之间能够交换信息。xcoms通过’pushed’(sent)和’pulled’(received)来传递变量数据。当一个task push xcom,它变能够被其他task所可用。task通过调用xcom_push()方法或者通过直接从task中的python_callable函数中获取其返回值。
1 | def push(**kwargs): |
而获取xcom通过
1 | ti = kwargs['ti'] |